|
Questions 1-7:
ATCase kinetics.
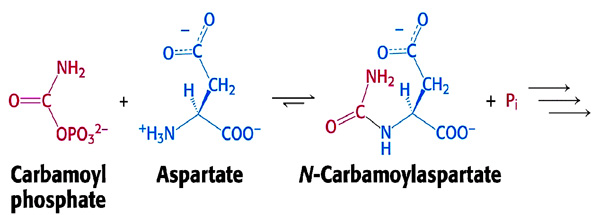
Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase)
catalyzes the condensation of carbamoylphosphate (CP)and Aspartate
(Asp) as co-substrates in the biosynthesis of N-carbamoylaspartate,
which is one of the intermediary precursors in the multi-step biosynthesis of
cytidine triphosphate (CTP) as indicated below.
|
-
The activity of this
enzyme is affected by two regulatory molecules -- ATP
and CTP.
-
Disulfide blocking
agents, like HgNO3, also affect the enzymatic activity
of ATCase.
-
For this exam,
consider the rates of product formation
catalyzed by ATCase when analyzed in the presence of varying
Asp concentrations, [Asp], with a fixed carbamoylphosphate
concentration, [CP], in excess over the total enzyme
concentration, [E]tot.
-
With a fixed [CP]
excess over [E]tot, the reaction becomes essentially
2nd order in terms of [Asp] and [E].
Open the
Hill plot showing the
experimental kinetic data obtained for ATCase catalysis under
varying conditions as indicated. Examine this plot to answer the
following questions. Note: The adjustable
green ruler line corresponds to
the Hill equation for this enzyme. Use this line to help you answer these
questions. |